Top Three Stress Relief Techniques
August 17, 2021
What is the Cardiovascular System?
October 29, 2021Stroke or Cerebrovascular Accident is a condition that happens when the brain fails to receive oxygen from the blood due to interruption, bleeding or blockage. As a result, the brain tissues start to die within minutes. Stroke is an emergency and needs urgent medical attention because every minute that the patient remains untreated equates to a portion of the brain that can no longer be revived.
In the United States, approximately 800,000 people suffer a stroke each year. About two-thirds of the individuals who suffered from stroke survive and require rehabilitation. This article will show you what to expect during the recovery and rehabilitation phase following a stroke incident when a more significant stroke occurs.
Recovering after stroke
A patient diagnosed with a stroke will have to be carefully monitored in an intensive care setting during the first hours up to days (or weeks). The period of recovery varies greatly on the injury sustained by the brain during the attack. If the patient was treated immediately, there is a greater chance of a shorter recovery period compared to those who weren’t able to receive medical attention quickly.
During the recovery stage, the patient will undergo various medical procedures, including a possible surgery to locate the area of bleeding or blood supply interruption within the brain and stop it from causing further damage. This stage is also crucial in determining the prognosis of the patient.
Possible long term or permanent effects of stroke
- Paralysis of the body (left-sided, right-sided, or both sides) can include weakness or total immobility
- Loss of memory or trouble remembering
- The trouble with judgment, awareness, attention, thinking, and learning
- Problems with swallowing and chewing
- Speech problems
- Pain along the hands and feet that gets worse with motion or temperature changes
- Numbness and tingling sensations along the extremities
- Bowel and bladder control issues
- Depression
Rehabilitation
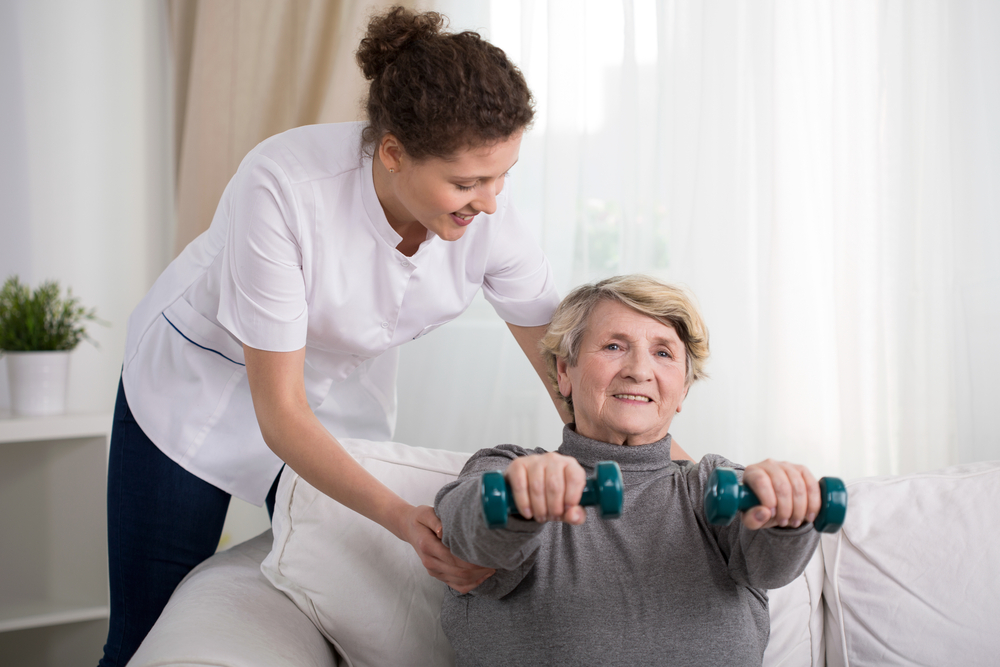
When a stroke patient successfully survives that vital period of recovery, he or she will undergo rehabilitation to regain some of the body’s functionality. The rehabilitation program includes speech, occupational, and physical therapy.
Speech Therapy
Speech therapy exercises greatly help those patients who suffer from a stroke. With these techniques, patients can relearn how to make sounds, form words, and breathe properly during speech. Speech therapy aims to help the patient regain control over communication by using speech patterns rather than signals.
Learning speech after a stroke can be difficult and frustrating; hence the best way to achieve noticeable and lasting improvements is through the help of a Speech Pathologist.
Physical Therapy
Physical therapy targets the patient’s movements by restoring muscle integrity and strength and easing the flexion and extension along the joints.
The goal of physical therapy is to help the patient readapt to simple movement and motor activities such as walking, standing, sitting, and lying down.
A stroke patient can remain in the hospital bed for weeks up to months. Because of this inactivity for an extended period, the muscles within the arms and legs lose their tone, and the joints start to stiffen. A physical therapist helps in moving these parts of the body by doing passive range of motion exercises so the stiff joints will loosen and the muscles regain their firmness.
Once the patient recuperates and develops enough strength to stand up with assistance, the physical therapist will assist in teaching strategies on how to perform gross motor movements. These include walking and lifting the legs and arms to move the body from one position to another. The physical therapist also guides the patient in performing these activities while ensuring that the patient maintains proper body posture and alignment to prevent injury.
Occupational Therapy
Occupational therapy targets fine motor movements to improve the patient’s daily activities such as eating, drinking, dressing, bathing, and writing.
The occupational therapist works closely with the patient and the family to determine the activities that are necessary, meaningful, and relevant. Using their expertise and the philosophical foundation of their profession, the occupational therapy practitioner analyzes the patient’s environment to structure an individualized approach that will cater to the occupational demands of the patient.
Many stroke survivors experience challenges in their emotions and cognition, making it difficult for them to learn even the basic means of feeding and grooming themselves as well as performing leisure activities.
The goals of an occupational therapist include the following:
- Retaining self-care skills
- Addressing any ongoing problems with weakness, sensory loss, visual impairments that may prevent the patient from performing activities of daily living
- Helping the patient adjust and adapt to the working environment or planning a different approach so the patient can remain work productive
- Developing strategies for continuous sexual intimacy
- Educate and promote healthy lifestyle habits to reduce the risk of a secondary stroke
- Developing methods to help the patient cope psychosocially
Most of the stroke survivors face multifaceted challenges in going back to their old life. Stroke rehabilitation is an interdisciplinary approach that requires the cooperation of the patient, the medical team, the family, and close friends of the patient. The Maplewood Sauk Prairie Health and Rehabilitation Center is an institution specialized in rehabilitating stroke patients. If you need help recovering from a stroke, schedule your consultation today.
References:
https://www.cdc.gov/
https://www.nia.nih.gov/
https://www.aota.org/
https://www.healthline.com/